Introduction
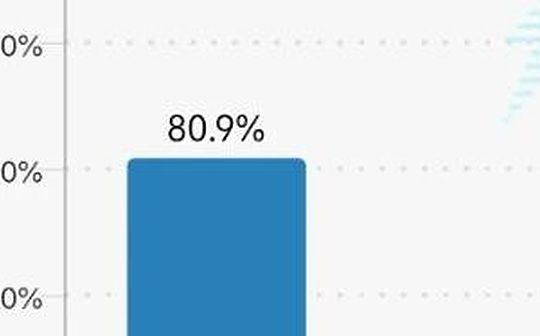
In the context of global economic recovery and uncertainty, the Fed’s monetary policy trends have always affected investors’ nerves.The current date is August 25, 2025, and according to the latest data from the CME FedWatch tool, the next Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting will be held on September 17, 2025.Currently, there is about an 82.9% probability that the Fed will cut interest rates by 25 basis points (bps), while the probability of keeping interest rates unchanged is only about 17.1%.This expectation is consistent with the volatility over the past month, which has gradually increased from lower probabilities at the beginning of the year to current highs.Other sources show similar trends, such as an 87.3% probability of a rate cut, reflecting concerns about an economic slowdown.
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate cuts are nothing new, but their consequences involve many aspects, including the stock market, precious metals (such as gold, silver), cryptocurrencies (such as Bitcoin), bond markets, consumer interest rates, and inflationary pressures.This article provides in-depth analysis and commentary on these impacts based on historical data and current market dynamics.It is worth noting that even if there is no interest rate cut in September, the October meeting will be the next key node, and an interest rate cut will come sooner or later.Historical experience shows that interest rate cuts often mark the start of loose monetary policy, which will drive up asset prices but may also exacerbate inflation risks.
Impact on the stock market
The impact of the Federal Reserve’s interest rate cuts on the stock market is one of the biggest focuses for investors.Historically, when interest rates are cut when the stock market is close to all-time highs (less than 2% from ATH), market performance shows a pattern of short-term volatility and long-term improvement.According to past statistics, the stock market fell by an average of 0.2% after one month, almost flat; rose by 2.1% after three months; rose by 3.8% after six months; and rose by an average of 13.9% after twelve months.What’s even more striking is that over the twelve-month time frame, the stock market has delivered positive returns 100% of the time.This means that if investors sit on the sidelines in anticipation of a market crash, time will increasingly be working against them.
Taking the current market as an example, the stock market has hit new highs many times in the first half of 2025, with technology stocks and growth stocks leading the gains.If an interest rate cut is implemented in September, the market may be volatile in the short term because investors have already digested some of the benefits in advance.However, in the medium to long term, interest rate cuts will reduce corporate financing costs, stimulate investment and consumption, and promote corporate profit growth.In terms of commentary, this historical pattern is not an iron law, but considering the current abundant global liquidity and the drive of emerging technologies such as AI, the possibility of “different this time” is low.Instead, we may be in the midst of a “great meltup” phase, with money printing in full swing and stocks continuing to benefit.
However, the risks cannot be ignored.If interest rates are cut too quickly, it could trigger an asset bubble to burst.Investors should note that the probability of a stock market rise after one month is only 45%, rising to 75% after three months and 100% after twelve months.Therefore, it is recommended that you consider buying dips in the short term, but long-term allocation is still king.For example, the trend chart of the S&P 500 Index over the past 30 years shows that each easing cycle is accompanied by a new high in the index, which is closely related to the inflationary effect of interest rate cuts.
Impact on Gold, Silver and Bitcoin
Interest rate cuts are often seen as a signal of inflation, which directly benefits non-yielding assets such as gold, silver and Bitcoin.Recently, hints of the Jackson Hole conference (although it is in 2024, its impact continues to this day) have pushed gold prices soaring.The price of gold has not really appreciated over the past 30 years, but has been the result of the dollar’s depreciation.As expectations of interest rate cuts increase, gold prices have approached recent highs and silver has risen above $39 per ounce.Bitcoin and altcoins also rebounded as interest rate cuts weakened the dollar, pushing commodities and risk assets higher.
Why is a rate cut inflationary?Simply put, lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, increasing the money supply.Even if some question the money supply (M2) expansion, the fact is that it is already growing.Comment: This is not a coincidence, but an inevitable result of monetary policy.In a weak U.S. dollar environment, the value of gold as a safe-haven asset is highlighted.As “digital gold”, Bitcoin’s scarcity and decentralized characteristics make it perform outstandingly during inflationary periods.Historical data shows that during the interest rate cut cycle, gold and silver prices rise by an average of 15-20%, and Bitcoin’s rise is even more impressive, often exceeding 50%.
Current market dynamics support this view.As the U.S. dollar index fell, commodity prices generally rose.If the Fed turns to quantitative easing (QE), this effect is expected to be further amplified in 2026.My point is that investors should not doubt this trend but plan for it early.Skeptics can look back to this analysis video from five months ago, which explains in detail how cutting interest rates inflates asset prices.
Impact on bond markets
The bond market is the most direct transmission channel for Fed policy.Expectations of rate cuts have caused bond yields to slide, especially short-dated Treasuries.The 3-month Treasury yield fell after the Jackson Hole, which is good for short-term government borrowing.The 10-year Treasury yield also continues to fall and is highly correlated with mortgage rates.Although the 30-year bond yield will be less affected, it can be pushed down further if the Fed expands its balance sheet.
This is good for government finances.President Trump has repeatedly urged the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates to reduce interest payments.Currently, the U.S. debt is huge, and lowering interest rates will ease the pressure.But for investors, rising bond prices (and falling yields) represent capital gains opportunities for holding long-term bonds.On the other hand, a rapid rate cut could distort markets and increase duration risks.
Overall, the bond market will enter an era of low yields, stimulating the economy but also challenging institutions such as pension funds seeking yield.Historical correlation shows that the Fed’s funds rate and the 10-year yield have a strong linkage, and interest rate cuts will gradually be transmitted to the entire yield curve.
Impact on consumer interest rates
The trickle-down effect of interest rate cuts will benefit consumers.Mortgage rates have fallen to this year’s lows, in line with the 10-year Treasury yield.Auto loan and credit card interest rates will follow suit, although credit card interest rates will still be higher (average above 20%).On the other hand, the yields on savings accounts and CDs will decline, affecting savers’ income.
Taking specific data as an example, the past trend chart shows that for every 25bps decrease in the Fed’s funds rate, mortgage interest rates will decrease by 15-20bps on average.This will stimulate the housing market and push up home prices as lower monthly payments attract buyers.Auto loans Likewise, lower interest rates will boost auto sales.Comment: This double-edged sword.On the one hand, lowering borrowing costs stimulates consumption and promotes economic growth; on the other hand, it intensifies debt accumulation, which may trigger crises in the future.
For brokerage accounts such as ESV, the yield will decrease with interest rate cuts.Investors need to adjust their strategies and turn to stocks or alternative assets.Generally speaking, interest rate cuts are good news for low- and middle-income groups, but they are a challenge for retirees who rely on fixed income.
Impact on inflation and the overall economy
The core consequence of interest rate cuts is inflationary pressures.Loose policies have weakened the U.S. dollar, causing prices for imported goods to rise and pushing up overall prices.Historical experience shows that after interest rate cuts, the inflation rate increases by 1-2% on average.At present, the expansion of money supply has become a fact, and combined with geopolitical risks, inflation may return.
The Fed’s “cut interest rates first, then QE” path will further devalue the US dollar.An official statement from Jackson Hole shows that they are preparing for the easing.This is not panic, this is reality.Asset price inflation will continue, but we need to be alert to the risk of stagflation.If the soft landing fails, rate cuts may not be enough to reverse the recession.
Cutting interest rates will benefit risk assets but increase systemic risks.Investors should diversify their allocations and focus on gold and Bitcoin as hedging.The government will benefit, but long-term debt sustainability is at issue.
Conclusion
The Fed’s interest rate cut is a turning point in the economic cycle, with consequences that go far beyond the surface.Based on historical and current data, the stock market is positive in the long term, gold, silver, and Bitcoin are benefiting, and bond and consumer interest rates are falling, but inflation risks are rising.Investors need to be cautious and seize opportunities rather than wait for a crash.Looking to the future, loose policies will dominate, but although there are voices saying “it’s different this time”, it’s hard to beat the data.Ultimately, monetary policy is a double-edged sword that requires balancing growth and stability.