Authors: Zhou Hao, Sun Yingchao

Since the advent of Bitcoin in 2009, blockchain technology has evolved from a single point-to-point electronic cash system to a diversified public chain ecosystem, covering the evolution of consensus mechanisms, scalability optimization (such as Layer-2, sharding), the introduction of interoperability protocols, and the continuous improvement of sustainability and security.The main differences in public chains are at present in terms of consensus mechanism, transaction processing speed (TPS), scalability solutions, security priorities, degree of decentralization and interoperability. These differences determine their unique positioning and trade-offs in scenarios such as store of value, DeFi applications, high-frequency trading or cross-chain collaboration.At present, major public chains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, Cardano, Polkadot, Avalanche, Cosmos and BNB Chain have formed their own unique competitive advantages, promoting the explosive growth of DeFi, NFT, Web3 games and cross-chain applications.
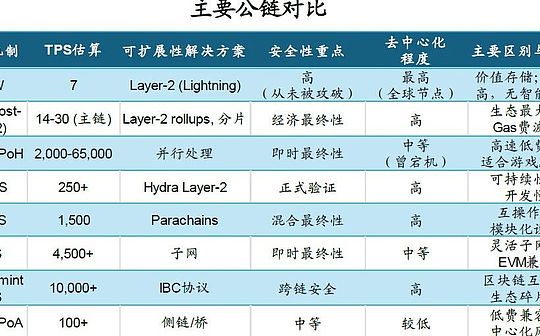
Core indicators of public chain issuance
The consensus mechanism is an algorithm that ensures that all nodes agree on the state of the ledger, replacing traditional centralized trust in a decentralized environment.It determines the security, decentralization and performance of the network.The original consensus mechanisms mainly include PoW and PoS.Proof of Work (PoW) ensures security through computing problems, but has high energy consumption; Proof of Stake (PoS) reduces energy consumption by staking tokens and relies on economic incentives; other variants such as DPoS, NPoS and PoH further optimize efficiency and scalability.The consensus mechanism directly affects the transaction speed, security and decentralized trade-offs of the chain.
TPS (Transactions Per Second) measures the ability of blockchain to process transactions and is a key indicator for evaluating its performance.High TPS means faster transaction confirmation and higher throughput, suitable for high-frequency applications (such as DeFi, gaming), but may sacrifice decentralization or security.Low TPS chains prioritize security, relying on Layer-2 and other solutions to improve actual performance.TPS is jointly influenced by consensus mechanism, ledger model and network architecture.
Scalability in the blockchain field refers to the ability of public chains to process large amounts of transactions, users and data while maintaining efficient, low cost and reliable performance.The scalability challenge of blockchain stems from the distributed nature of decentralized networks, that is, each node needs to verify and store all transaction data, resulting in performance bottlenecks.For example, Bitcoin’s block size (1MB) and block time (10 minutes) limit its TPS to only 7, while the Ethereum main chain is also limited by high gas fees and congestion.Scalability is a key link in solving the “triad dilemma” of blockchain (decentralization, security, and scalability), and it directly affects the performance of public chains in high-frequency applications.The current main solutions include: on-chain expansion, off-chain expansion, side chain and subnet, and cross-chain interoperability.These plans have their own advantages and disadvantages when facing the “triple difficulties”, and are also important considerations when issuing different stablecoins.
Bitcoin: The founder of digital gold
Bitcoin is the first public chain, launched by Satoshi Nakamoto on January 3, 2009.As the pioneer of blockchain technology, its core goal is to create a decentralized digital currency system to avoid the centralized risks of traditional finance.Bitcoin adopts the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, where miners verify transactions and add blocks by solving complex mathematical puzzles.This mechanism ensures network security, but also leads to high energy consumption problems – according to market estimates, the annual energy consumption of Bitcoin networks is equivalent to that of a medium-sized country.on the other hand,Bitcoin’s limitation is its weak programming ability and its inability to support smart contracts, which makes it lag behind its juniors in fields such as DeFi.
Key features include:
-
Ledger status: Use the UTXO (Unspended Transaction Output) model to emphasize the immutability of transactions.
-
TPS: About 7 TPS, the transaction confirmation time can reach 60 minutes.
-
Scalability solution: Relying on the Layer-2 protocol, it is used for off-chain payment channels, and improving actual throughput.
-
Advantages: Extremely high security (never successfully attacked by 51%) and decentralization (ten thousand nodes around the world).Bitcoin’s native token, BTC, is regarded as “digital gold” and is mainly used for store of value rather than complex applications.
Ethereum: The pioneer of smart contracts
Ethereum was launched by Vitalik Buterin on July 30, 2015 and is the “operating system” of the public chain ecosystem.It introduced the Turing-complete smart contract, allowing developers to build decentralized applications (DApps), which gave birth to the DeFi and NFT revolution.Ethereum initially used PoW consensus, but was upgraded to Proof of Stake (PoS) on September 15, 2022, called Ethereum 2.0, which greatly reduces energy consumption (99% reduction) and improves security.Ethereum’s disadvantages are its high volatility in Gas fees and high congestion, but its developer community and EVM compatibility make it the industry standard.
Key features include:
-
Ledger Status: Account balance model, easy to track user assets.
-
TPS: Main chain is about 14-30 TPS, but Layer-2 solutions such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon zkEVM can push the actual TPS to thousands.
-
Scalability solutions: sharding and Layer-2 rollups, alleviating congestion through parallel processing and off-chain computing.The Pectra upgrade in 2025 further optimizes stability.
-
Advantages: A huge ecosystem (more than thousands of DApps).ETH tokens are used for Gas fees and support cross-chain bridging.
Solana: High-performance “Ethereum Killer”
Launched on March 16, 2020, Solana was founded by Anatoly Yakovenko, aims to solve the triad of blockchain (decentralization, security, scalability).It combines PoS with the original Proof of History (PoH), which achieves instant finality through time stamp optimization block verification.Solana’s inferiority lies in its single-chain architecture, emphasizing speed, but the network has been down due to congestion, which has caused doubts about decentralization.
Key features include:
-
Ledger status: Account balance model, supports Rust and C programming.
-
TPS: Theoretically up to 65,000 TPS, the actual processing is about 2,000-4,000 TPS, and the confirmation time is less than 1 second.
-
Scalability solutions: parallel processing and Sealevel runtime, processing massive transactions without sharding.In 2025, its ecosystem will expand to DeFi, NFT and gaming.
-
Advantages: Low fees (less than $0.01 per transaction) and high speed make it suitable for high-frequency applications.
Other important public chains
Cardano is known for its academic rigor, adopting the peer-reviewed Ouroboros DPoS consensus, emphasizing sustainable development.Its layered architecture and Hydra Layer-2 solution can be scaled to one million TPS, but the slow development pace has affected ecological growth.
Polkadot realizes the interoperability of heterogeneous blockchains through the unique design of connecting multiple parachains with relay chains.Its NPoS consensus mechanism supports a full network throughput of approximately 1,500 TPS, which is suitable for enterprise-level cross-chain applications.
Avalanche’s three-chain architecture and subnet design provide high flexibility, and its EVM-compatible features make it a popular choice for Ethereum project migration, with 4,500+ TPS and confirmation time in 2 seconds showing strong performance.
Cosmos is committed to building a “blockchain Internet”. Its IBC protocol and Hub model realize seamless communication between different blockchains, with a theoretical TPS of more than 10,000.
With its deep integration with the Binance ecosystem and EVM compatibility, BNB Chain provides a low-gas fee trading environment, but its relatively centralized verification mechanism has also caused controversy.
To be sure,There is huge room for development of blockchain. As an important component, public chains are also a general trend to shift their competition from single chain to multi-chain coexistence and development.In the short term, Ethereum will still dominate, but innovations from other platforms can also pose unignorable challenges to Ethereum, and interoperability and sustainability will become the focus of competition among various public chain platforms.But no matter what, these public chains will reshape finance, technology and society, and promote the formation of a deeper decentralized world.








