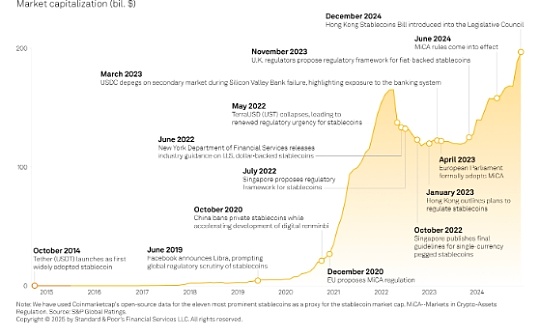
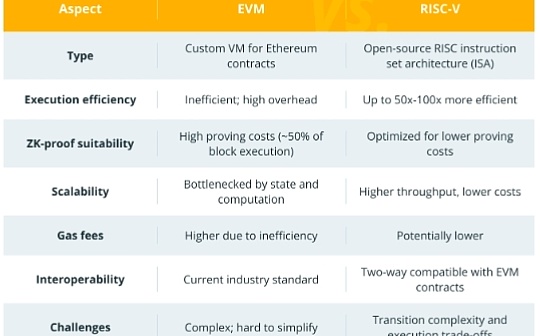
Author: James Smith, CoinTelegraph; Compilation: Wuzhu, Bitchain Vision
1. Analysis of tokenized products
Tokenized commodities represent partial ownership of real-world assets using digital tokens on blockchain, while retaining their tangible value.
Tokenized commodities are digital versions of real-world items (such as gold, oil, or crops) recorded on the blockchain.Each token represents part or all of the commodity, making it easier to split and trade.This simplifies the buying and selling of a small portion of the investors’ commodities, provides more liquidity, and provides opportunities to enter markets that are often difficult to trade.
Imagine you have a giant pizza that you can’t eat alone.Instead of giving the whole pizza to one person, you cut it into slices.Now everyone can buy and enjoy the right amount of food that suits their appetite.
Tokenized physical goods work similarly.Commodities such as gold or oil are giant pizza.Instead of buying the entire item (which can be very expensive and impractical), you split it into small pieces called tokens.Each token represents a small portion of the commodity.
2. Tokenization process
Have you ever considered owning a small portion of a barrel of oil or a small portion of a bar of gold?These are tokenized commodities, a combination of blockchain technology and traditional assets.
Tokenized commodities have become digital tokens, opening up new channels for trading and access for investors.Here are the steps involved in the tokenization process:
-
Create tokens:Create tokens representing products.One way to achieve this is to establish the identity of the property owner as a legal entity.Tokens enable holders to share the value of the goods.
-
Smart contract execution:Smart contracts enable the allocation, monitoring and payment of digital token rewards.Once started, these programs run without intervention.
-
Token distribution and sales:Tokens are distributed to investors through smart contracts through combinations of private sales, public sales or whitelisting models.A whitelist is a setting that allows only pre-approved or trusted users, entities, or operations to run.
-
asset Management:After the token is sold, new holders can participate in managing the basic goods.Smart contracts specify the scope of control and decision-making process of token holders.
-
Secondary market transactions:After the token is issued, it can be traded on the secondary market to create liquidity.Unlike traditional commodity investors who may have difficulty selling assets, token holders can sell their shares more easily.
3. Types of tokenized products
Blockchain technology can help tokenize a variety of commodities, including energy resources, real estate, precious metals and agricultural products.
Let’s explore various tokenized commodities:
-
Precious Metals:Tokenize precious metals such as platinum, gold and silver, allowing investors to hold small amounts of precious metals without physical storage.This helps diversify and hedge portfolios while also increasing accessibility to these assets.
-
Energy Resources:Tokenizing energy is the conversion of actual energy (such as solar or wind) into digital units on a digital platform.This facilitates new energy-related use cases such as exchanging excess solar energy among neighbors, simplifying renewable energy credit and improving grid management.
-
Agricultural resources:Blockchain implements tokenization of agricultural resources and creates a security record representing products exchanged on digital ledgers.This brings efficiency, security, openness and cost reduction to retail investors’ commodity trading.
-
real estate:Investors can tokenize properties by dividing them into smaller parts and using smart contracts to automate operations.Records are stored in a secure digital system.The owner can prove his ownership using a private key.Anyone interested in buying, leasing or financing can easily view the property’s history with this system.Past transactions about the property, including any outstanding debts, are displayed as transparent and non-changeable records.

4. Tokenized commodities and cryptocurrencies supported by commodities
Commodity-backed cryptocurrencies are digital assets designed to be more stable than volatile cryptocurrencies.This stability is achieved by linking its value to tangible commodities such as real estate, gold or oil.
A company or organization holds an actual product and issues tokens representing a specific quantity of that product.The value of the token fluctuates with the cost of the underlying commodity.
For example, both the cryptocurrencies supported by commodity Tether Gold and Pax Gold are backed by actual gold.Similarly, other cryptocurrencies can be backed by commodities such as oil reserves or other valuable commodities.
The following table explains the difference between tokenized commodities and cryptocurrencies supported by commodities:

5. Benefits of commodity tokenization
Commodity tokenization defines ownership, realizes partial ownership, simplifies transactions and promotes market activities.
Let’s take gold-backed tokens as an example to understand the advantages of commodity tokenization.
-
Liquidity enhancement:One of the major advantages of tokenized commodities is increased liquidity.By converting commodities such as gold into digital tokens, these assets can be easily traded on the blockchain platform.This allows investors to buy and sell some goods without an intermediary, thereby reducing transaction costs and transaction time.
-
Partial ownership:Partial ownership is another important advantage of tokenized commodities.It allows more investors who may not have the funds to buy a complete unit to buy goods.This makes it easier for investors to access commodities, allowing them to diversify their portfolios.
-
Better security and transparency:Tokenization uses blockchain, which is like a digital notebook that records every transaction.This notebook cannot be changed, ensuring transparency and security as everyone can see who owns what.
-
Easier to trade:Traditional commodity trading methods can be time-consuming and complex.Digital tokens allow users to easily trade anytime, anywhere, making the investment process simpler.
6. Risks of tokenized goods
Although the prospects are bright, tokenized commodities also face challenges.Rules are not always clear, as existing rules may not fully cover them.The technology behind tokenized commodities must be properly tested to deal with the complexity of creating and trading these tokens.
Continue to take gold-backed tokens as an example, let’s dive into the risks associated with tokenized commodities.
-
Liquidity:If the secondary market is not enough to handle transaction volume, tokenization is of no use.Establishing market depth requires trust between institutional investors and traditional market participants using blockchain technology.
-
Standardization and interoperability:The smooth integration of tokenized commodities and existing financial systems requires standardization and interoperability.Compatible token standards, smart contracts and data formats between various blockchain platforms and commodity markets are essential for efficient transaction settlement and asset transfer.
-
Cybersecurity:Protecting the integrity of tokens, private keys, and sensitive transaction data requires powerful security measures such as encryption and two-factor authentication (2FA).Continuous monitoring is required to prevent theft, hacking and exploitation.
-
Regulatory Challenges:Tokenized physical goods are subject to securities, commodity trading and financial market laws.To comply with these laws, strong governance mechanisms must be established to prevent fraud, market manipulation and regulatory violations.