Author: Xinwei, Severin, Ian, MT Capital
TL;DR
-
Celestia currently shows a solid pledge trend with a pledge rate of 48.88%, an annualized pledge return (APR) of 15.74%, and is predicted to reach the ideal pledge rate limit by the end of 2024.Since there will be no new token unlocking by 11 months of 2024, it is expected that the actual circulation of its tokens will continue to decrease, thus having a positive impact on the price.Meanwhile, the Celestia network currently maintains 100 active nodes.
-
Celestia currently has data usage at just 0.1% of total daily capacity, and despite this, its activity is growing compared to Ethereum.As data usage increases, expenses may increase significantly in the future. If the data capacity reaches 46,080 MB per day for the whole year, the annual cost will be as high as about US$5.2 million, which is 65 times the current Ethereum data cost.User demand is expected to come from high TPS applications and games, with a large number of chains based on Celestia RaaS emerging in the coming months.
-
EigenDA’s adoption of erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD and other technologies, as well as the decoupling of DA from consensus, enables EigenDA to provide excellent performance far exceeding Ethereum DA solutions in terms of transaction throughput, node load and DA costs.Compared with other DA solutions, EigenDA also has the advantages of lower startup and staking costs, faster network communication, data submission speed and greater flexibility.
-
Compared with Celestia and EigenDA, Celestia’s competitive advantage lies in its extremely low data availability cost and higher data throughput, which makes Celestia more popular among small and medium-sized L2 and application chains.EigenDA’s competitive advantage lies in potentially higher security and Ethereum orthodoxy, which makes EigenDA a rational choice for more large-scale L2 revenue and reduction.In the future, Celestia will be able to enjoy the gains of the incremental market brought by the dual trend wave of modularity + application chain, while EigenDA will gain more Ethereum-based stock markets with higher security requirements.
-
The NEAR protocol enhances scalability and decentralization through sharding technology and stateless verification, simplifying data management for L2 projects.Avail optimizes blockchain data processing and storage through a modular system, supports asynchronous interaction between application chains, improves network performance, and enables light clients to effectively verify data integrity.Together, these technologies have promoted the user-friendliness and decentralized digital world of blockchain technology.
introduction
The data availability layer has become an important part of the modular architecture, and DA has gradually become one of the hottest tracks in 2024, and discussions on Ethereum DA, Celestia and other DA solutions are emerging in the market.This article will conduct in-depth discussions on the core mechanisms, characteristics, comparisons and future development expectations of Celestia and EigenDA, the core players of the DA track, and scan other players of the DA track to help readers take a look at the current development of the DA track and understandThe future competitive landscape of DA track.
Celestia
Celestia is the first modular data availability (DA) network designed to scale securely with the growth of user numbers.This modularity allows anyone to easily launch a standalone blockchain.
Celestia Technical Features
-
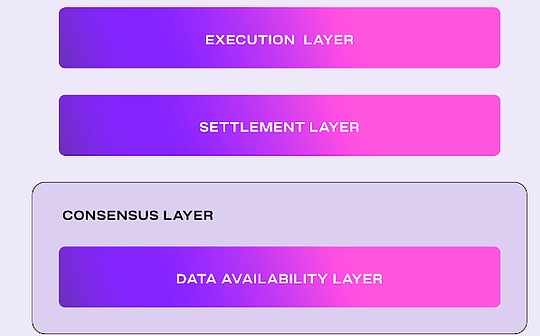
ModularDAnetworkCelestia’s design separates execution, consensus, settlement and data availability.This modular structure allows specialization and optimization at every level, improving the overall efficiency and scalability of the network.

source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/monolithic-vs-modular
-
Data availability sampling (DAS)DAS is a method that allows light nodes to verify data availability without downloading the entire block.Light nodes randomly sample data blocks, which if this data can be successfully retrieved and verified, means that the data for the entire block is available.

source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
-
Namespace Merkel Trees (NMTs)NMTs enable block data to be divided into separate namespaces for different applications.This means that applications only need to download and process data related to them, greatly reducing the data processing needs.

source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
-
Scalability through light nodesWith more light nodes participating in data availability sampling, the more data the network can process.This scalability feature is essential for maintaining efficiency as the network grows.
-
Proof of fraud for error extension dataTo deal with possible data extension errors (whether intentional or unintentional) by block producers, fraud proof allows verification and rejection of blocks with invalid data, enhancing network security.
-
Build for data availabilityPoSBlockchainCelestia uses PoS blockchain, called celestia-app, to facilitate transactions and data availability.This layer is built on celestia-core, an improved version of the Tendermint consensus algorithm designed to handle the unique needs of the DA layer.
-
Scalability
There are two decisive factors for scalability: the amount of data sampled in a centralized manner (the amount of data that can be sampled) and the size of the target block header of the light node (the size of the light node directly affects the performance and scalability of the overall network).
In view of the above two factors, Celestia uses the principle of collective sampling, that is, by participating in partial sampling of data through many nodes, it can support larger data blocks (i.e. higher transaction processing volume per second, tps).This approach can expand network capacity without sacrificing security.Furthermore, in the Celestia system, the size of the block header of the light node grows proportional to the square root of the block size.This means that if you want to maintain nearly the same security as the full node, light nodes will face bandwidth costs proportional to the square root of the block size.
Features of the modular Celestia Stack
-
Self-SoulCelestia’s Rollups are different from Ethereum Rollups, and their specification state is determined independently when they run on Celestia.This increases autonomy, allowing nodes to freely decide how they operate through soft and hard forks.This self-sovereignty reduces dependence on central governance and promotes more experimentation and innovation.
-
flexibilityCelestia’s execution-independent features mean that its Rollups are not limited to EVM-compatible designs.This openness provides a broader space for virtual machine innovation and helps promote technological development.
-
Easily deployCelestia simplifies the deployment process of blockchain.With tools like Optimint, developers can quickly deploy new chains without worrying about the complexity and high costs of consensus mechanisms.
-
Efficient resource pricingCelestia separates the growth of activity status and historical data storage, providing a more efficient resource pricing mechanism.This approach reduces the mutual impact between execution environments and improves the user experience.
-
Trust minimization bridgeCelestia’s architecture supports the creation of a bridge of trust minimization, allowing different chains to be securely interconnected.This enhances the security and interoperability of blockchain clusters.
-
Minimum governanceCelestia’s modular design reduces the need for centralized governance.The executive layer can develop independently and rapidly, while the consensus layer remains stable, and this separation reduces the need for complex social coordination.
-
Decentralized block verificationCelestia emphasizes the decentralization of block verification, not just block production.This approach increases the security and trustworthiness of the network.
-
SimplicityCelestia chose simple and mature technologies such as Tendermint as its basis to avoid overcomplexity.This simplicity is conducive to the stability and scalability of the system.
Celestia’s data cost
Numia Data recently released a report titled “The impact of Celestia’s modular DA layer on Ethereum L2s: a first look”, which compares the different Layer 2 (L2) solutions released on Ethereum over the past six months.The costs incurred by CallData and the possible costs incurred if they use Celestia as the data availability (DA) layer (in this calculation, assume the TIA price to $12).By comparing the cost differences in the two cases, this report clearly demonstrates the huge economic benefits of a dedicated DA layer like Celestia for reducing L2 Gas costs.

source: https://medium.com/@numia.data/the-impact-of-celestias-modular-da-layer-on-ethereum-l2s-a-first-look-8321bd41ff25
Token Economics
The totality of the creation of the worldSupply:1 billion TIA.
The distribution of TIA at the time of creation

source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply

inflationplan:Starting at 8%, then drops by 10% annually until it reaches its annual minimum of 1.5%

source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply
TIA’s token utility
-
Pay the data space fee:Developers submit PayForBlobs transactions on Celestia, using TIA to pay fees to use their data availability tier.
-
Boot the new Rollup:Developers can use TIA as Gas tokens and currencies to launch new blockchains, similar to ETH used in Rollup based on Ethereum.This helps focus on the development of the application or execution layer without the need to issue new tokens immediately.
-
Proof of Stake:Celestia is built on the Cosmos SDK and uses proof of stake to guarantee its consensus.Users can delegate TIA to validators and earn a portion of the pledge rewards.
-
Decentralized governance:TIA holders participate in governance, vote to determine network parameters and manage community pools, which receive 2% block rewards.
Token unlock

source: https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply

PledgeCondition
Celestia’s current staking rate is 48.88%, and its staking APR is 15.74%.

source: https://staking-explorer.com/staking/celestia
Based on the current relationship between pledge APR and pledge rate, the following linear relationship is fitted:
Staking APR = -0.3331 * Staking rate + 0.3204

source: MT Capital
It is known that the minimum staking APR of Celestia is its own inflation rate, at 7.85%.The ideal limit for obtaining a pledge rate is 72.6%.
Based on the data on the pledge rate changing over time, it can be seen that the pledge rate reaches its limit by about the end of 24 years.

source: MT Capital
And because Celestia would not have a new unlocking situation before 11 months, we can think that before 11 months, the actual circulation of Celestia would continue to decrease, and we are paying the token price of Celestia before 11 months, 2014.Continue to be optimistic.
Currently, the number of active nodes in Celestia is 100.

source: https://wallet.keplr.app/chains/celestia
Compared with the Ethereum main network, Celestia data costs are reduced by 99.9%.Users can publish data to blobs containing namespaces and access data by filtering specific namespaces.Since Celestia has been running for two months, users have published a lot of data to different namespaces, but 87% of them are concentrated in three main namespaces.

source: https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864
Celestia currently has just 0.1% of data usage per day, which is much lower than the 46,080 MB of data it can support per day.Nevertheless, Celestia’s activity is still growing compared to Ethereum’s current 15 Rollups and 700 MB of data per day.
Currently, Celestia costs are relatively low, but if data usage increases, the costs may increase significantly.If Celestia achieves annual data capacity of 46,080 MB for a TIA price of $13, the network will incur an annual fee of about $5.2 million.This will be 65 times the data currently published to Ethereum.The cost structure of the network may lead to bidding wars between users, thereby pushing up costs.
Future user needs may come from various applications such as high TPS universal chains, specific applications or games.While it is difficult to predict specific sources of demand at present, gaming and high TPS Rollup may be key drivers.In the coming months, we will see a flood of chains leveraging Celestia’s RaaS launches coming into the market.

source: https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864
Celestia’s newValuation Model
Considering that Celestia is the first modular public chain DA layer, and the Cosmos community is very generous to Celestia stakers (Dymension’s airdrops have covered the cost of Celestia stakers), there will be a large number of modular public chain-related issues in the future.The project will airdrop the Celestia stakeholders, so there will be the following valuation ideas:
Price (TIA) = Accumulation of value to the DA layer + TIA’s currency premium as a “modular currency” + the value of all future airdrops
Celestia Ecological Project
Cevmos
Cevmos is a rollup stack developed by Evmos and Celestia, the Cosmos EVM application chain, with the goal of providing the best settlement layer for EVM-based rollups on Celestia.This name is composed of the abbreviations of Celestia, Evmos and Cosmos.Cevmos aims to provide a dedicated settlement layer for rollups to reduce costs and increase efficiency as part of its mandatory settlement rollup scheme.Cevmos is a settlement layer, built on Evmos and implements recursive rollup of EVM on top of it.
Unlike the existing Tendermint Core consensus engine on Cosmos, Cevmos adopts Optimint (Optimistic Tendermint), an alternative to Tendermint BFT that allows developers to deploy rollups with existing consensus and data availability such as Celestia.Since Cevmos itself is a rollup, all rollups built on it are collectively called settlement rollups.Each rollup reduces migration workload by minimizing two-way trust bridges with Cevmos rollups.All rollups will use calldata on Cevmos rollup, and Cevmos batches the data through Optimint and publishes it to Celestia.
As a constrained EVM environment, Cevmos rollup also attempts to address challenges with a single-round fraud proof.Cevmos not only avoids designing and maintaining complex consensus mechanisms, but also brings the efficiency of rollup and the interoperability of EVMs to the entire Cosmos ecosystem, providing a practical and modular solution for the widespread application and popularity of the Cosmos ecosystem.

source: https://blog.dodoex.io/understanding-the-modular-blockchain-celestia-ecosystem-construction-9eb583eaea6b
Dymension
Dymension is a Cosmos-based sovereign rollup platform designed to greatly simplify application-focused custom rollups (called “named “customized” rollups with its Dymension Chain (closing layer), RDK (RollApp Development Kit Development Kit) and IRC (inter-rollup communication) capabilities.for the development process of rollApp.
Dymension’s autonomous construction settlement layer, called Dymension hub, is a chain that adopts the Tendermint Core state replication model and is based on the PoS consensus mechanism.RollApp built on Dymension hub not only inherits the security of hub, but also realizes communication between each other through RDK and dedicated module groups supported by hub.
RollApps consists of two key components: the client and the server.As the application end of RollApp, the server side is responsible for implementing custom business logic and building the pre-packaged module of the RollApp development toolkit RDK.The client component, called dymint, is derived from Optimint of Celestia. As a direct replacement for Tendermint, it is responsible for block production, peer-to-peer network messaging and inter-layer communication.Since RollApp itself does not undertake consensus tasks, dymint can provide the low latency performance required for modern applications.
Similar to Cosmos, the goal of Dymension RollApps is to create application-specific blockchains to reduce consensus overhead.RDK adds new modules and modifys existing modules based on the Cosmos-SDK to ensure RollApp compatibility with the Dymension protocol while still remaining compatible with other Cosmos ecosystem tools.RollApps are able to interact with any IBC-enabled chain through the Dymension Hub, so they are also part of the Cosmos ecosystem.

source: https://blog.dodoex.io/understanding-the-modular-blockchain-celestia-ecosystem-construction-9eb583eaea6b
Eclipse
Eclipse is a sovereign rollup project based on the Cosmos ecosystem, which specifically allows the use of Solana VMs on any chain to build customizable modular rollup billing layers.In its early stages, Eclipse planned to use Celestia as its consensus layer and data availability (DA) layer, while using Solana VM as an environment for execution and settlement.The ultimate goal of Eclipse is to provide customized rollup execution layers for different Layer1 heterogeneous blockchains, connecting various blockchains through a modular approach.In addition, Eclipse plans to further develop Solana VM-based billing layer rollup into Optimistic rollup and zk rollup in the future, thereby expanding its capabilities and application scope.

source: https://blog.dodoex.io/understanding-the-modular-blockchain-celestia-ecosystem-construction-9eb583eaea6b
Fuel
Although Fuel and Celestia are similar, they have obvious differences.Celestia focuses on optimization of data availability and consensus, handling data sorting, while Fuel is positioned as a modular execution layer.
One of the main differences between Fuel is the new virtual machine architecture it runs – FuelVM, and the accompanying Sway language and toolchain.FuelVM is a custom virtual machine designed specifically for executing smart contracts, capable of processing transactions in parallel and designed from the very beginning to prevent fraud, suitable for transaction execution layer of Optimistic rollup.
FuelVM combines the SeaLevel features of WASM, EVM, and Solana, but its uniqueness is the use of the UTXO model rather than the account model.This means that Fuel VM requires each transaction to specify the UTXO it will contact.Because the execution engine is able to accurately identify the state involved in each transaction, it can easily identify uncontroversial transactions that are processed in parallel.This design makes Fuel VM more efficient and secure when handling transactions.

source: https://blog.dodoex.io/understanding-the-modular-blockchain-celestia-ecosystem-construction-9eb583eaea6b
Celestia Summary and Future Outlook
Celestia, the first modular DA network, focuses on expanding securely as the number of users grows.Its modular design makes it easy to start a standalone blockchain.The network’s core technologies include data availability sampling (DAS) and namespace Merkel trees (NMTs). The former allows light nodes to verify data availability without downloading the entire block, and the latter allows applications to process only relevant data., greatly reduces data processing needs.
According to the relationship between the current staking rate and APR, it is expected that Celestia will not have new unlocks before November 2024. According to the current staking trend, Celestia’s staking rate will continue to rise, and the actual circulation will continue to decrease. It is expected that its token price will beContinue to rise.In addition, Celestia has reduced data costs by 99.9% compared to the Ethereum mainnet, and its daily data usage rate is only 0.1%, which is far lower than the 46,080 MB of data that can be supported per day, showing huge expansion potential.
The value of Celestia’s TIA token is not only based on its application and innovation in blockchain technology, but also the airdrop value it may obtain in the future.With the development of blockchain technology and the further popularization of modular public chains, Celestia and its TIA tokens may show greater potential and value.
In the Celestia ecosystem, several innovative projects such as Cevmos, Dymension, Eclipse and Fuel are included. These projects use Celestia’s modular nature to provide customized solutions for specific applications, reflecting Celestia’s importance in the field of blockchain technologyStatus and development potential.
Given its unique approach and technological innovations, Celestia is expected to play an important role in the blockchain industry.Its focus on solving the three problems of blockchain, especially scalability, without sacrificing security or decentralization, making it an important player in the ever-evolving blockchain ecosystem.
EigenDA
Introduction to EigenDA
EigenDA is EigenLayer’s first AVS product.EigenDA aims to rely on Ethereum’s security to make the restaken node a validation node of EigenDA, and supports Rollup to publish data to EigenDA to obtain lower cost and higher transaction throughput data availability services.
EigenDA Technical Architecture
EigenDA follows the final expansion path of Ethereum Danksharding. Therefore, the technical path of the DA layer adopted by EigenDA is also highly related to the technical path of Ethereum Danksharding expansion.Furthermore, EigenDA’s adoption of technologies such as erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD (Authenticated Coded Dispersal) and decoupling of DA from consensus can provide far exceeding Ethereum Danksharding in terms of transaction throughput, node load and DA costs.Excellent performance of DA scheme.
The specific implementation process of EigenDA is as follows:
-
First, after the Rollup’s sorter creates the data blob, it needs to send a request to split the data blob to the Disperser.(Disperser can be run by Rollup itself, or you can use third-party Disperser such as EigenLabs)
-
Secondly, after receiving the data blob, the Disperser needs to split the data blob into different data blocks, and use erasure code to generate redundant data blob data blocks, as well as corresponding KZG commitments and KZG multiple-revealproofs).
-
Next, Disperser will distribute the data block, KZG promise and KZG multiple reveal proof to different EigenDA nodes (Ethereum re-staken nodes are registered as EigenDA nodes).EigenDA nodes require the use of KZG multi-revealing proof and the KZG promise to verify the validity of the data block.After verification is correct, the node needs to save the data and send the signature to the Disperser.
-
Finally, Disperser aggregates the signature and sends it to the EigenDA contract on the Ethereum mainnet.The signature in the EigenDA contract will be further verified, and the process will end if the verification is correct.

source: https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/intro-to-eigenda-hyperscale-data-availability-for-rollups/
Similar to the ideas of other DA solutions, EigenDA’s core idea is to use DAS technology to reduce the storage and verification load of a single node, while increasing the throughput of global DA consensus, and using redundancy of erasure code to ensure data security.The difference is that EigenDA has chosen the KZG commitment verification technology that is the same frequency as Ethereum in terms of specific technical choices.Moreover, EigenDA does not rely on consensus protocols and P2P network propagation, but uses unicast to further improve consensus speed.
In addition, EigenDA has some more refined designs in ensuring node data storage and node verification.
EigenDA ensures that the EigenDA nodes actually store data in data blocks through Proof of Custody.Each EigenDA node must periodically calculate and submit the value of a function, and the node must store the corresponding data block to calculate the value of the function.The ETH of a node that fails to pass the Proof of Custody will be fined.
EigenDA further guarantees the effectiveness of DA consensus through Dual Quorum proof.EigenDA will have at least two independent sets of Quorums to prove data availability.For example, one group of Quorums consists of ETH restakers and the other group consists of Rollup native token stakers.Two independent Quorum DAs must be verified simultaneously to be valid.
EigenDA Feature Analysis
To better distinguish between the differences and advantages and disadvantages of EigenDA and Ethereum DA and other DA solutions, we compare the two separately.
Comparing Ethereum DA, EigenDA:
-
EigenDA nodes do not need to download and store all data, but only need to store a small piece of data, which significantly reduces the operating and operational costs of the node.
-
EigenDA decouples DA from consensus, so that nodes can directly and parallelly process the proof of data block availability, thereby significantly improving network operation efficiency.Moreover, through erasure coding and KZG promise, nodes only need to download small pieces of data for storage and verification, and network throughput is higher.
-
Since EigenDA only inherits part of the mainnet security, from the perspective of security, EigenDA is still weaker than Ethereum DA.

source: https://medium.com/@VendingMachine/avs-token-design-considerations-eigenda-compared-to-celestia-89d416059758
Comparing other DA solutions, EigenDA:
-
The nodes of EigenDA are a subset of re-staked nodes in the EigenLayer network. It does not require additional pledge costs to become EigenDA nodes.
-
EigenDA decouples DA from consensus and directly unicasts, so that the propagation of data blocks is no longer limited by consensus protocols and P2P network throughput, which can greatly shorten communication, network latency and confirmation time and improve data submission speed.
-
EigenDA inherits some Ethereum security, and in general, it is more secure than other DA solutions.
-
EigenDA also supports Rollup to flexibly select different staking token models, erasure coding ratios, etc., with higher flexibility.
-
Since EigenDA’s final confirmation relies on the EigenDA contract on the Ethereum mainnet, EigenDA will be significantly higher than other DA solutions in terms of final confirmation time overhead.
EigenDA latest developments and use cases
EigenDA launched testnet tests with mid-November 2023.Initially, EigenDA limited the number of node operators on the test network to 30 and set a target of initial throughput of 1Mbps.EigenDA plans to gradually expand the number of operators so that EigenDA can eventually approach its target throughput of 10Mbps.
At present, according to data from the EigenDA test network, the number of node operators on the EigenDA test network has expanded to 200, but the average network throughput in the past 7 days was only 0.45Mbps, which has not yet reached the initial target of 1Mbps.

source: https://blobs-goerli.eigenda.xyz/?duration=?P7D
At present, the total TVL in the EigenDA test network is about 3.5M, among which the LST of Ankr, Lido and Stader are the top three pledged assets with the largest proportion.The total number of node operations reached 200, and the total number of pledged people reached 29.4k.

source: https://goerli.eigenlayer.xyz/avs/eigenda
Although EigenDA is still in the test network stage, we might as well compare the current test network data of EigenDA with the relevant data of Ethereum to see how far EigenDA is from its final vision.
-
Inheriting the security of Ethereum:
-
Currently, the TVL of EigenDA test network is about 3.5M, while the FDV of Ethereum is about 264B. From the perspective of asset value, EigenDA only inherits 0.001% security of Ethereum.
-
Currently, the number of pledged verification nodes on the EgenDA test network is 29.4k, while the number of pledged verification nodes on Ethereum is 904k. Judging from the number of pledged verification nodes, EgenDA inherits about 3.2% of Ethereum’s security.
-
Improved network throughput:
-
Currently, the throughput of EigenDA test network is about 0.45Mbps, while Ethereum’s throughput is about 0.083Mbps. Although EigenDA’s network throughput is still ideal for 1Mbps – 10Mbps or even the final 1Gbps, compared with Ethereum’s throughputThere is still about 500% improvement.
Currently, EigenDA has launched a partnership program, and eight project parties, AltLayer, Caldera, Celo, Layer N, Mantle, Movement, Polymer Labs and Versatus, have reached a cooperation with EigenDA to plan to use EigenDA’s data availability services.
Summarize
EigenDA’s adoption of erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD and other technologies, as well as the decoupling of DA from consensus, enables EigenDA to provide excellent performance far exceeding Ethereum DA solutions in terms of transaction throughput, node load and DA costs.Compared with other DA solutions, EigenDA also has the advantages of lower startup and staking costs, faster network communication, data submission speed and greater flexibility.EigenDA is expected to carry some DA services in Ethereum and become a new competitor in the DA market.
Celestia vs. EigenDA and future prospects
DAcontrast:
Data availability sampling:
Celestia supports data availability sampling, allowing light nodes to randomly sample data blocks for download and verification.EigenDA does not support data availability sampling.Supporting data availability sampling allows Celestia to safely increase block size with more light nodes, ensuring the minimum requirements for node verification without increasing node burden.The increase in the number of light nodes can also increase the degree of decentralization of the network.
Coding proof scheme:
Celestia uses fraud proof mode to ensure that the original data is correctly encoded, while EigenDA uses KZG promises for validity proof.In contrast, Celestia’s fraud proof has a lower threshold and a relatively higher level of technology maturity, and does not require the additional cost of generating KZG promises.But using KZG promised EigenDA will be faster in verifying data accuracy than Celestia, which uses fraud proofs, because under the fraud proof mechanism, light nodes need to wait a short time before they can receive fraud proofs from the full node.
Consensus mechanism:
Celestia uses the Tendermint consensus mechanism and requires point-to-point network communication propagation.EigenDA decouples DA from consensus and directly unicasts, so that the propagation of data blocks is no longer limited by consensus protocols and P2P network throughput, and network communication time and confirmation time are faster.
However, EigenDA needs to rely on the EigenDA contract on the Ethereum main network to complete the final verification confirmation. Therefore, in terms of the final confirmation time of blocks, Celestia only takes 15 seconds, which is significantly faster than EigenDA’s 12 minutes.

source: https://forum.celestia.org/t/a-comparison-between-da-layers/899
Node load:
Since the full nodes of Celestia need to undertake the functions of broadcasting, consensus and verification at the same time, Celestia has 128MB/s download and 12.5MB/s upload data bandwidth requirements for the full nodes.However, EigenDA nodes do not need to be responsible for the functions of broadcasting and consensus. Therefore, EigenDA’s bandwidth requirements for nodes are very low, only 0.3MB/s.
Throughput:
Celestia’s data throughput is approximately 6.67MB/s.EigenDA’s current test network throughput is 0.45MB/s, which is still a certain gap from the expected target of 1MB/s – 10MB/s.At this stage, Celestia’s throughput has significant advantages over EigenDA.
Startup Cost:
Celestia’s DA solution is highly dependent on the security of its PoS network, so it must pledge sufficient Tia tokens to become a Celestia node.Celestia’s DA solution has certain startup costs.
The security of EigenDA is inherited from Ethereum. To become an EigenDA node, you only need to pledge the node registration, without paying additional pledge costs, avoiding the initial startup cost.
Cost of use:
Celestia currently charges Manta a DA cost of $3.41/MB.According to data from the EigenDA test network, the current cost of using EigenDA is about 0.024 Gas/Byte.In contrast, Celestia’s DA solution still has huge cost advantages over EigenDA.
Security:
Celestia’s security is guaranteed by its network value.The higher the network value of Celestia, the higher the cost of attackers’ attacks, and the smaller the probability of the attack success.Currently, the staking value of Celestia is about 1.2B, which means that malicious attackers need to pay at least 0.8B to attack the Celestia network.
EigenDA is a subset of Ethereum security for security.The size of EigenDA security depends on the value of re-staking assets in the EigenDA network and the proportion of node operators on the Ethereum main network.From the TVL perspective, as far as the current test network data is concerned, EigenDA’s network value only inherits Ethereum’s 0.001% security.If EigenDA wants to achieve more than Celestia’s current security, the value of re-staked assets in the EigenDA network needs to account for more than 0.45% of the Ethereum network value.Currently EigenDA is still in the test network stage, and EigenLayer has limited asset deposits open.It is expected that after the EigenDA main network is launched and EigenLayer is fully released, the value of re-staking assets in the EigenDA network will further surge, surpassing Celestia in terms of network security.
Of course, the number of nodes is also one of the factors that cannot be ignored in network security.Currently, the number of pledged verification nodes in Celestia is about 100, and the number of nodes in the EigenDA test network is 200.From the perspective of the number of nodes, EigenDA will also be better than Celestia.

source: MT Capital
Although Celestia and EigenDA currently have different solutions in data availability sampling and coding proof solutions, the choices of the two may be more convergent as DAS and KZG technologies continue to mature.According to @sreeramkannan, EigenDA will also consider introducing DAS in the future to support more light nodes.@likebeckett also shows that if the validity proof scheme based on KZG promises becomes more attractive than fraud proof, Celestia can also change its coding proof scheme.Therefore, the differences in the DA technical architecture of the two may not become the core difference in the future.
The most significant difference in the future between the two is more likely to be the gap in network security, the gap in usage cost, and the gap in throughput.
DAFuture Outlook:
Based on our comparison of Celestia and EigenDA in the previous section, network security, usage cost and throughput may become the core considerations for different projects to choose different DA solutions.In addition, Ethereum orthodoxy that EgenDA itself has is also one of the key factors that cannot be ignored.
From the perspective of network security, although the current network security demonstrated by EigenDA test network is still far behind Celestia.But we believe that with the launch of the EigenDA main network, EigenLayer’s relaxation of re-pending assets restrictions and the explosion of resting narratives in the second half of the year, the value of assets pledged in EigenDA will increase exponentially, and the number of nodes in EigenDA will also be significantIncrease.EigenDA’s network security may far exceed that of Celestia.Projects that rely more on security may favor EigenDA’s solutions.
-
Currently, Ethereum’s FDV is about 277B, and it is obviously very easy to achieve only 0.4% of Ethereum participating in EigenDA.
In terms of the cost of use gap, the current cost of Celestia is still significantly lower than that of EigenDA.Small L2, which is more profit-sensitive and more application chains may prefer Celestia’s DA solutions.The migration of Lyra and Aevo to Celestia DA is the best example.Profitability is first and foremost an issue that every small and medium-sized L2 must consider.In the early stages when there was no sufficient prosperity for the ecosystem to generate income, increasing revenue and reducing expenditure was undoubtedly the wisest choice. Blindly pursuing Ethereum’s “brand premium” may hinder its own development.For the application chain, lower cost expenditure also gives the application chain more room for asset control, and can more flexibly formulate profit sharing incentives, liquidity incentives, and user activity incentives based on its own development to guide its own value.The development of the network.
-
Taking aevo as an example, migrating to Celestia can reduce its data availability cost by 90%+.

source: https://medium.com/@numia.data/the-impact-of-celestias-modular-da-layer-on-ethereum-l2s-a-first-look-8321bd41ff25
In terms of throughput gap, Celestia’s throughput still has a significant advantage of more than 10 times based on the existing Celestia throughput data and EigenDA testnet throughput data.Celestia, which has higher throughput, will obviously be more favored by application chains with higher performance requirements.Moreover, Celestia can also flexibly increase the block size according to actual needs, providing higher scalability and transaction throughput to the application chain.Of course, EigenDA’s test network data can only be used as a reference at present. EigenDA can sometimes perform 6MB/s – 8MB/s.The specific performance still needs to wait for EigenDA to finally be launched, so that a more fair judgment can be made during actual operation.
In terms of Ethereum orthodoxy, projects using EigenDA will still be regarded as having orthodox Ether blood.However, as time goes by and the concept of modularity deepens, the situation of being scoffed or scolded as a rebellious person because of the use of Celestia DA is expected to gradually decrease. The concept of orthodox Ethereum will be massive L2 and massive application chains in the future.It gradually blurs in the wave.However, in the short term, it should be difficult for us to see the migration of DeFi on Ethereum and the L2 kings. Grasping Ethereum is still one of their core narratives.
To sum up, Celestia is very lowDACost and higherThroughputPerformance makes Celestia very attractive to small and medium-sized L2 and application chains.The L2 and application chains that save high DA costs have more room for asset control, which can better distribute revenue and profits to stimulate the development of their respective ecosystems and liquidity.In contrast, EigenDA’s competitive advantage relies more on security and orthodoxy attached to Ethereum.In the short and medium term, EigenDA may become a more rational choice for large L2s than Ethereum’s expensive DA.
Therefore, after detailed comparison, we believe that Celestia can enjoy more of the incremental market gains brought by the dual trend wave of modularity + application chain, while EigenDA will eat more Ethereum with higher security requirementsIt is the stock market.
Nowadays, the competition between Celestia DA and Ethereum DA has gradually become the focus of market discussion.In addition, third-party DA solutions such as Near DA and Polygon Avail have also begun to surface one after another.This article will continue to play the remaining paths of the DA’s development, Near DA and Polygon Avail, the main players of third-party DA.
NearDA
Cost-effective
Using NEAR DA can significantly reduce the cost of data storage and transfer.The cost of publishing a Block calldata on NEAR is only $0.0016, while the cost of publishing the same amount of data on Ethereum L1 (after the Cancun upgrade) is about $7.73, indicating that NEAR is as cost-efficient as 5000 times.

source: https://near.org/data-availability
Technical Principles
The Blob Store contract is a key component on the Near blockchain and is designed to process and store DA blobs.The Blob Store contract stores blobs by leveraging Near’s consensus mechanism, and when a block producer processes a data, consensus is formed around that data.
Data pruning: Once the block contains the receipt and is processed, the receipt no longer needs to be used for consensus and can be pruned.The time for pruning is at least 3 NEAR epochs, each epoch is 12 hours, and in fact it is usually five epochs.
Archive node: Once the receipt is pruned, the responsibility for storing transaction data is transferred to the archive node.This data can also be obtained from the indexer.
Blob Commitment Verification: By checking blob commitments, we can verify that blobs are retrieved from ecosystem participants in the format submitted.The blob promised creation method is to split a blob into 256-byte fragments and create a Merkel tree where each leaf is a sharded Sha-256 hash.The root of the Merkel tree is a blob commitment, provided to the L1 contract in the form of [transaction_id ++ commitment], which is 64 bytes of data.
Key Advantages
-
Consensus Verification: Near validates providing consensus around blob submissions.
-
Data persistence: Function input data is stored by the full node for at least three days, and the archive node can store data for a longer period of time.
-
Efficient use of consensus: Consensus that does not consume more data than is needed.
-
Indexer support: This data is currently indexed by all major browsers on NEAR.
-
Long-term availability of commitments: Commitment is easy to create and easy for anyone to build with limited expertise and tools.
At present, Near’s data availability layer product NEAR DA has been integrated with developer stacks such as Polygon CDK and Arbitrum Orbit, which developers can use to build their own L2 or L3 networks, etc.
NEAR-Polygon CDK integration allows developers who build their own rollups to become part of the Polygon ecosystem, the first integration of NEAR DA with the ZK-based L2 stack, adding selectivity to developers looking for scalable DA solutions.This integration is also built on the NEAR-Polygon research collaboration to build zkWASM—a new prover for the WASM blockchain.In the future, builders can even create NEAR DA-based zkWASM chains.NEAR DA and zkWASM technologies will play a key role in parallel scaling the EVM and Wasm ecology while maximizing the interoperability of multi-chain futures.
The Arbitrum Orbit chain utilizes the Arbitrum Nitro technology stack, a technology developed by Arbitrum to scale Ethereum.It allows developers to create their own blockchains that can settle transactions on Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova, or Ethereum mainnet, provided that Arbitrum DAO grants an L2 license.These Orbit chains use Arbitrum’s Rollup and AnyTrust protocols to provide customization in throughput, privacy, gas tokens and governance to meet specific use cases and business needs.For example, rollup developers looking for cheaper data availability (DA) alternatives can now take advantage of NEAR DA in the Arbitrum Orbit stack.In this way, developers can build self-managed, configurable blockchains with more control over their functions and governance while gaining security assurance from Ethereum.
Polygon Avail
Avail was originally a project by Polygon in 2020 and became a standalone entity in 2023.The team, led by Anurag Arjun, co-founder of Polygon and Prabal Banerjee, former head of research at Polygon, aims to provide industry-leading data availability solutions.Polygon Avail is a modular blockchain solution focused on the data availability layer, aiming to build scalable data availability solutions.It adopts a range of technologies including light client, data availability sampling, KZG (Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg) polynomial commitment and erasure coding, etc., to improve the throughput of on-chain data and solve performance bottlenecks.

source: https://blog.availproject.org/the-avail-vision-reshaping-the-blockchain-landscape/
Avail’s design features include:
-
Consensus mechanism: Use BABE and GRANDPA consensus mechanisms from the Polkadot SDK, combining activity and security to provide network resilience and ability to withstand temporary network partitions and large number of node failures.
-
Decentralization: Polkadot’s nominated proof of stake (NPoS) supports up to 1,000 verification nodes and reduces the risk of stake centering through effective reward allocation.Avail’s full node and light client use the Data Availability Sampling (DAS) method for verification, allowing the same security as traditional full nodes while reducing dependency on full nodes.
-
Proof of validity: Avail uses KZG polynomials to promise to reduce memory, bandwidth and storage requirements, providing an efficient verification process.This is different from the fraud proof technology used by Celestia, where Avail has many similarities at the data availability level, but its core difference lies in the method of proof of effectiveness.
-
Data availability and security: Avail’s design philosophy focuses on establishing a data availability layer and provides a universal data availability solution.It does not rely on most assumptions of honesty, and light clients can determine data availability by themselves through random data sampling, and can rebuild blocks from light nodes even if full nodes are down or attempted to review data.
-
Technology implementation: Avail uses data redundancy, anti-fraud proof and commitment mechanisms to ensure data validity.It ensures that the data remains valid after “erase” through KZG polynomial commitment, including data redundancy, anti-fraud proof, and commitment mechanism, so that the full node can be included in all transaction data of the light node.
The practical applications of Avail include hosted independent chains, side chains and off-chain expansion solutions, with the goal of providing the application layer with a full-scenario data availability solution.For example, in the Ethereum Layer 2 solution, Avail can be used for transaction sorting and data availability, ensuring data availability on the chain while reducing data volume limits on the main chain.
NearDAFuture Outlook with Polygon Avail
The NEAR protocol demonstrates its scaling capabilities and future development through its sharding method and NEAR DA technology.The recent shift to stateless verification by the engineering team marks a further development of sharding technology, aiming to achieve more sharding and a higher degree of decentralization by reducing the hardware requirements of validators and transferring state to memory.This will improve the overall processing power of the NEAR protocol, allowing projects and developers to avoid competing for block space.As the number of shards increases, the data storage requirements for a single shard decrease, and in theory each account may become its own shard, allowing lightweight RPC nodes to run.This means more efficient data management for L2 projects using NEAR DA.Although data availability sharding is still in the R&D stage, it has demonstrated the important advantages of the NEAR protocol for various builders and ecosystems.With the development of the Web3 field, NEAR has not only solved the scaling challenges facing Ethereum, but also prepared for the future of multi-chain and cross-chain, promoting NEAR DA technology by providing rollup with fast and low-cost data availability solutions.Placed at the forefront of this change.
Avail’s future outlook focuses on improving efficiency and accessibility of the blockchain ecosystem.Through its modular system, Avail aims to independently optimize data processing and storage to improve overall network performance.It emphasizes in particular on enhancing data availability and ensuring that data can be effectively verified even if it is not stored directly on the chain, which is crucial to maintaining transaction transparency and security.Avail also plans to support asynchronous interactions of multiple application chains, similar to microservice architectures, to improve overall flexibility and scalability.For ordinary users, Avail enables light clients to verify data integrity through advanced technology without downloading the entire blockchain, which makes blockchain technology more user-friendly.Since being independent of Polygon, Avail has begun exploring new collaboration opportunities with diverse partners to demonstrate its potential in multiple application scenarios.Ultimately, Avail’s goal is to provide developers with an easy-to-use environment that inspires them to create innovative applications while promoting a more open, connected and decentralized digital world.
Reference
https://www.chaincatcher.com/article/2111784https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/monolithic-vs-modular
https://staking-explorer.com/staking/celestia
I spent some time in the trenches with @CelestiaOrg data and have some random thoughts on what the future looks like👇 pic.twitter.com/DW5YusiGSf
— Dan Smith (@smyyguy) January 8, 2024
https://docs.eigenlayer.xyz/eigenda-guides/eigenda-rollup-user-guides/building-on-top-of-eigenda
https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/intro-to-eigenda-hyperscale-data-availability-for-rollups/
https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/launch-of-the-stage-2-testnet-eigenlayer-eigenda/
https://www.reflexivityresearch.com/free-reports/exploring-eigenlayer
https://medium.com/@VendingMachine/avs-token-design-considerations-eigenda-compared-to-celestia-89d416059758
https://forum.celestia.org/t/a-comparison-between-da-layers/899
https://mirror.xyz/edatweets.eth/zZG84zO6EjGo9sieBvHUEYYjsY1935n2XMkc_12_678
(Usecase-5) EigenDA: It is possible to combine trust models 1 and 2 to create new services. EigenDA built on @eigenlayer uses a dual quorum model, where one quorum can be run by ETH staking economic quorum and another quorum can be run by @Rocket_Pool ETH stakers.
— Sreeram Kannan (@sreeramkannan) November 24, 2022
https://blog.celestia.org/ethereum-off-chain-data-availability-landscape/
https://www.odaily.news/post/5189320
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/45728
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/45308
https://www.panewslab.com/zh/articledetails/z7f4srnb.html
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/52079
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/51570
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/42095
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/20581
I spent some time in the trenches with @CelestiaOrg data and have some random thoughts on what the future looks like👇 pic.twitter.com/DW5YusiGSf
— Dan Smith (@smyyguy) January 8, 2024
https://near.org/blog/near-foundation-launches-near-da-to-offer-secure-cost-effective-data-availability-for-eth-rollups-and-ethereum-developers
https://near.org/data-availability
https://pages.near.org/blog/arbitrum-integrates-near-da-for-developers-building-ethereum-rollups/
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/51873
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/46036
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/48885
https://dodotopia.notion.site/Celestia-f86a7f5e0a154e229a2fddf9a90c37ea
https://docs.celestia.org/concepts/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
https://forum.celestia.org/t/an-open-modular-stack-for-evm-based-applications-using-celestia-evmos-and-cosmos/89
https://fuel-labs.ghost.io/beyond-monolithic-the-modular-blockchain-paradigm/
https://medium.com/alliancedao/the-case-for-parallel-processing-chains-90bac38a6ba4
https://docs.dymension.xyz/learn/dymension-hub
https://mirror.xyz/neelsalami.eth/rvhK5mEcFTOjyu_DFsqS2cYR7U6Fjvbw3nf8tI-pr-Q?ref=twitter
https://polygon.technology/solutions/polygon-avail/
https://rainandcoffee.substack.com/p/the-modular-world
https://www.techflowpost.com/article/detail_15557.html
https://medium.com/@numia.data/the-impact-of-celestias-modular-da-layer-on-ethereum-l2s-a-first-look-8321bd41ff25






