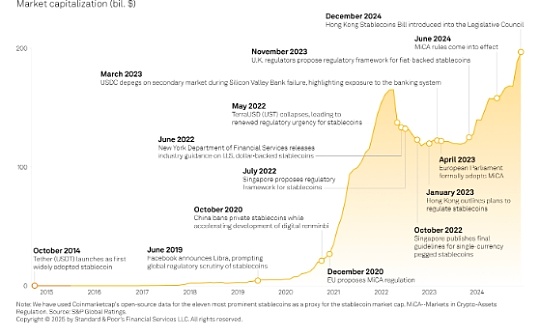
Source: CoinTelegraph; Compilation: Baishui, bitchain vision
1. Quantitative Easing (QE) Interpretation
Quantitative easing (QE) is a non-traditional monetary policy tool used by central banks, especially when interest rates are already low and cannot be further reduced.
It became popular during the 2008 global financial crisis, when traditional monetary tools such as lowering interest rates were not enough to stimulate economic growth.
The main goal of quantitative easing is to boost the economy by increasing the money supply.The implementation method is to encourage banks to increase lending and reduce borrowing costs for consumers and enterprises.When the central bank implements quantitative easing policies, it will purchase government bonds or other securities from the market and inject cash into the financial system.
Although people sometimes say that quantitative easing is like “printing money,” it is different from making new physical currencies.Instead, it increases the number of digital currencies in an economy, i.e. the balance in a bank account.This is not a cryptocurrency; it is a regular currency created by the central bank, which banks use to increase lending, which helps stimulate spending and investment.
Quantitative easing will also drive up prices for assets such as stocks and bonds, as additional funds seeking returns will drive up demand.During the COVID-19 pandemic, governments have also used quantitative easing policies to maintain economic stability and support growth.
two,How does quantitative easing policy work?
To understand how quantitative easing works behind the scenes, it is important to understand the progressive mechanisms that drive this policy.
Quantitative easing does not work with a single action—it works through a series of events that begin with the central bank and ultimately affect daily economic activities.This process is usually as follows:
-
Asset Purchase: Central banks purchase government securities, such as Treasury bonds, from banks and financial institutions.
-
Increase money supply: These purchases make the financial system liquid.
-
Lower interest rates: With more cash on hand, banks will lower interest rates and make loans cheaper.
Promoting loans and spending: Cheaper loans mean more business investment and consumer spending, the main driver of economic growth.
three,The practice of quantitative easing: historical cases
Quantitative easing is not just a theory—it has been used by major central banks during economic hardships.
Here are some real-world examples:
United States (2008-2014; 2020): Global Financial Crisis
After the collapse of the real estate market in 2008, the U.S. economy fell into a deep recession.The following measures can be helpful:
-
The Federal Reserve has introduced three rounds of quantitative easing policies (QE1, QE2, QE3).
-
It purchased trillions of dollars worth of government bonds and mortgage-backed securities.
-
This helps lower interest rates, support loans and boost stock markets.
When the COVID-19 pandemic caused the global economy to shut down, the Fed quickly took action:
-
It reintroduces quantitative easing, buying $120 billion in bonds a month at peak times.
-
The purpose is to keep borrowing costs low and support businesses and families.
Japan (2001-2006, and 2013-present): Fighting the Deflation
Japan has been facing problems of low inflation and weak growth for many years.The Bank of Japan (BoJ) said:
-
Quantitative easing policies began before most other countries.
-
A large number of government bonds were purchased, which later included stocks and real estate investment trusts.
Eurozone (2015-2022): Post-debt crisis recovery
After Greece, Italy and Spain suffered a debt crisis, the European Central Bank (ECB) introduced quantitative easing:
-
The ECB buys government bonds from euro zone countries to reduce borrowing costs.
-
This provides support for weaker economies, aiming to prevent deflation (decline in price).
Four,How quantitative easing affects the cryptocurrency market
Quantitative easing policies not only affect traditional financial markets, but also cryptocurrency markets.
When the central bank injects more money into the economy, some of the money flows into alternative assets such as Bitcoin and altcoins, pushing up its prices.As more funds are available for investment, a surge in liquidity often drives up the prices of all assets, including cryptocurrencies.
In addition, fiat currencies may depreciate due to increased money supply during quantitative easing, causing some investors to seek cryptocurrencies to hedge the risks of inflation or currency depreciation.Bitcoin, in particular, is often seen as a store of value similar to gold.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the Federal Reserve introduced radical quantitative easing policies.at the same time:
In March 2020, Bitcoin was trading below $5,000.
By the end of 2021, that price had soared to over $60,000.
Key factors in Bitcoin’s rise during quantitative easing include increased inflation concerns and low interest rates that prompt investors to turn to alternative assets.Among them, one of the main drivers may be the search for storage of value outside traditional finance.Therefore, quantitative easing can indirectly promote the prosperity of the cryptocurrency market by influencing investor sentiment and liquidity.
On the other hand: After the end of quantitative easing, cryptocurrencies may be affected.
When the central bank ends quantitative easing or starts hikes (sustainment policy), liquidity will decrease and borrowing costs will rise.This can lead to a callback for risky assets, including cryptocurrencies.
For example, in 2022, the Fed began to quantify austerity policies to deal with inflation.Bitcoin price fell from about $47,000 in March to below $17,000 in December — possibly due to investors’ shift to safer assets and a decline in risk appetite due to rising interest rates.

five,Quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT): main differences
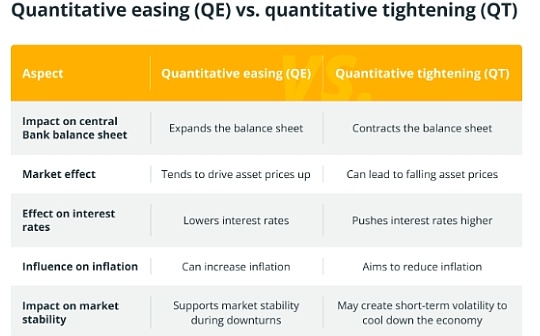
Quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative austerity (QT) are two opposite monetary policies adopted by central banks.
Quantitative easing policy refers to expanding the money supply by purchasing assets such as government bonds, thereby injecting cash into the economy to stimulate economic growth.Its main purpose is to lower interest rates and encourage loans when the economy is in trouble.
Quantitative easing (QT) is the process by which central banks reduce their balance sheets.It involves selling assets or letting them mature, thereby reducing the money supply.The goal of quantitative easing is to cool down an overheated economy and prevent inflation from rising too quickly.
The key difference between quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT) is their impact on the central bank’s balance sheet: quantitative easing expands the balance sheet, while quantitative tightening shrinks the balance sheet.In terms of market effects, quantitative easing often pushes up asset prices, while quantitative tightening can lead to decline in asset prices and rising interest rates.Both policies will significantly affect inflation and market stability.

Is the Fed’s reduction in bond purchases the same as quantitative easing policies?
No, reduction and quantitative easing are not the same—but they are interconnected.
-
Quantitative easing refers to the Federal Reserve actively purchasing assets such as government bonds, injecting funds into the economy and reducing interest rates.
-
Reduction refers to the Fed’s slowdown in asset purchases – this is the beginning of the end of quantitative easing, not a reversal.
6. Will the Fed tighten or easing in 2025?
As of April 2025, the Fed is facing a complex economic situation characterized by persistent inflationary pressures and slowing economic growth.
In response, the Federal Reserve maintained the benchmark interest rate in the range of 4.25%-4.50%, indicating that it is cautious about monetary policy adjustments.
Although the Fed has not completely turned to a loose stance, it has begun to slow down its quantitative easing.Specifically, starting from April, the Federal Reserve has reduced the monthly issuance of U.S. Treasury bonds from $25 billion to $5 billion, while continuing to allow $35 billion in mortgage-backed securities to mature without reinvestment.
Looking ahead, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) expects two rate cuts to be cut later in 2025, depending on the economic situation.This forecast reflects the Federal Reserve’s attempt to balance the dual mission of controlling inflation and supporting employment in the context of many uncertainties, including the impact of recent tariff policies.
7. Pros and cons of quantitative easing
Quantitative easing can promote growth and reduce borrowing costs, but overuse may exacerbate inflation, asset bubbles and long-term policy challenges.
advantage
-
Quantitative easing helps promote economic activity by increasing the money supply and encouraging lending and investment.
-
By purchasing government bonds, quantitative easing lowers interest rates, making borrowing costs for businesses and consumers lower.
-
By injecting liquidity into the economy, quantitative easing helps stimulate demand and support price stability and prevent deflation.
shortcoming
-
Excessive increase in money supply can lead to depreciation of the currency and drive up inflation.
-
Loose monetary policy will drive up asset prices, resulting in overvalued stocks, bonds or real estate.
-
Quantitative easing has increased national debt, making it more difficult for central banks to manage inflation or interest rates in the future.
Finally, quantitative easing remains a powerful but double-edged tool: it can stabilize economies in crisis, but also carries long-term risks that must be managed carefully to avoid repeating the same mistakes.