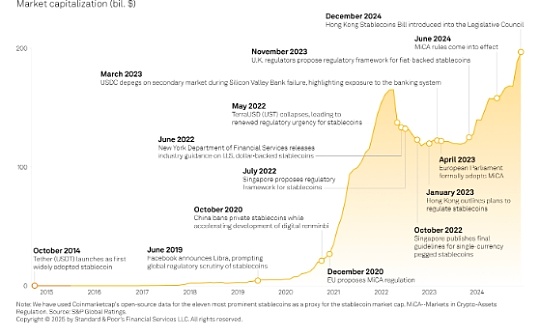
Source: Chainalysis; Compilation: Wuzhu, bitchain vision
In 1985, the original concept of Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) appeared in a peer-reviewed academic paper titled “The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems,” marking a breakthrough in cryptography.Researchers Shafi Goldwasser, Silvio Micali and Charles Rackoff explored whether it is possible to prove that the data is valid without revealing any information other than the data itself.Nearly 40 years later, ZKP has become a fundamental component of many blockchains, supporting users through enhanced privacy and security.
What is zero-knowledge proof?(ZKP)
Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) is an encryption method that allows multiple parties to verify the authenticity of a statement without revealing information outside the statement itself.Many blockchains utilize ZKP to improve the security of interactions involving sensitive data.Therefore, participants in blockchains with ZKP can interact with more confidence, as private information is unlikely to be leaked or exploited by malicious actors.
The components of zero-knowledge proof
ZKP requires at least two parties to participate in each interaction: the prover and the validator.The prover is responsible for providing actual mathematical proof to convince the validator of the validity of the statement.The validator must check this evidence and accept or reject it.
There are usually multiple rounds of communication between the prover and the verifier to reduce the possibility that either party speculates or provides illegal information.
How does zero-knowledge proof work?
ZKP operates using basic building blocks of advanced encryption algorithms and mathematical concepts.For example, ZKP uses cryptographic hash functions to generate random challenges for validators in an effort to build mutual trust with provers.
Interactions supported by ZKP must meet the following conditions:
-
Integrity:If the statement is true, an honest prover should be able to easily convince the validator.
-
Soundness:If the statement is false, a dishonest prover should not be able to deceive the verifier.
-
Zero knowledge:Neither party can extract other private information about each other; they only know what the statement is provided.
Let’s look at an example of how two users can use ZKP to trade:
-
A (Proofer) wants to use the privacy currency ZCash to execute the transaction so that no observer of the hidden blockchain can withdraw any details of the transaction (i.e., transfer amount, transfer address, etc.).
-
B (verifier) wants to receive ZCash from A but does not know their private details, such as the total assets held in A’s wallet.
-
A crypto transaction and submit it to the blockchain.
-
A Submit a ZKP with a crypto transaction to prove that the transaction is valid.
-
Nodes on the blockchain check ZKP to ensure that A’s crypto transactions are indeed valid.
-
If ZKP is valid, B will accept it.
-
ZCash transfers from A’s account to B’s account.
-
Transactions are permanently recorded on the blockchain.
Types of zero-knowledge proofs
ZKP mainly comes in two forms: interactive and non-interactive.Interactive ZKP involves multiple rounds of back and forth communication between prover and validator.Non-interactive ZKP involves only one round of communications – the proofor only sends a message to the verifier, and they don’t have to be online at the same time to happen.
Interactive proofs are not common in blockchain-based systems because they are inefficient and are often not desirable to require both parties to be online at the same time.Therefore, use the following types of ZKP in a non-interactive setup:
Zero-knowledge concise non-interactive knowledge argument (zk-SNARK) enables participants to demonstrate possession of certain information without revealing the details of that information.Zk-SNARK is common on the Ethereum blockchain and is especially useful for privacy-protecting smart contracts.ZCash also uses Zk-SNARK to prove the validity of protected transactions, such as those that do not disclose any information—including senders, recipients, and transfer amounts.
Zero-knowledge scalable transparent knowledge arguments (zk-STARK) function similarly to zk-SNARK but aims to scale large computing.Because of the additional advantages of zk-STARK such as transparency and scalability, it is compatible with a variety of blockchain applications.
Bulletproof proof proves that a value is within a certain range without revealing the value itself.By using advanced mathematical concepts, bulletproof proofs can make proofs smaller, thereby reducing transaction size and verification time.Monero uses bulletproof proof.
Application and use cases of zero-knowledge proof
Zero-knowledge proof offers a wide range of applications in the blockchain ecosystem, from decentralized protocols that enhance privacy to scalable transaction solutions.Although some of these use cases have been adopted by blockchain, others are still in the speculation stage or in the early stages of development.
Authentication and secure authentication:DeFi participants can use ZKP to prove that they have certain attributes, such as participating in governance activities or becoming members of a specific token holder group without revealing the actual value of these attributes.Likewise, users can interact with ZKP to selectively disclose information related to their identities.
Safe Voting System:ZKP allows DeFi participants to demonstrate their voting eligibility and number of votes without revealing their history or voting preferences.
Zk-rollupsIs the Layer 2 extension solution that bundles transaction data off-chain or “Rollup” as cryptographic proof, and then publishes transaction validity on the Ethereum main network in the form of calldata.Since transactions are published in bundles to the mainnet, they usually take up less space, reducing the computing burden on Ethereum.Popular zk-rollups include ZkSync and Loopring.
Zk-Plasmais a variant of the Plasma network that uses ZKP to create privacy-protected sidechains on Ethereum.Instead of verifying all data on the mainnet, users can verify transactions on the sidechain and then publish their validity on Ethereum using ZKP.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX):ZKP can facilitate transactions of various assets without revealing the user’s transaction history, strategy or account balance.
Supply Chain Transparency and Integrity Verification:ZKP can enhance the security of the supply chain by verifying the authenticity of the supplier’s credentials and products without the need to disclose transaction information or proprietary information about the production process to unauthorized parties.Additionally, ZKP may help verify certification and compliance with supply chain regulatory standards.
The following figure illustrates the scale of application of zero-knowledge technology in some use cases.We saw the amount of funds sent to several of the most popular ZKP applications, including ZCash (a privacy-protecting cryptocurrency), Tornado Cash (a decentralized, unmanaged smart contract), Railgun (Ethereum L2 privacy protocol) andAztec (Ethereum L2 Privacy Agreement).Between January 2022 and April 2024, more funds were sent to Tornado Cash than the other three ZKP-enabled apps, close to $5 billion.

Challenges of Zero Knowledge Proof Adoption
Although ZKP is expected to make blockchains safer and more efficient, its widespread adoption still faces many challenges:
-
Implementing and deploying ZKP requires a deep understanding of encryption principles and advanced math—most developers do not have this expertise.
-
Generating ZKPs often requires a large amount of computing resources, resulting in slower transaction processing times and increased fees.
-
Interoperability of blockchains can become difficult if participants encounter incompatible protocols or verification methods.
-
The complexity of ZKP and the corresponding data storage can pose regulatory compliance and audit challenges.
The future of zero-knowledge proof in blockchain
As awareness of the importance of privacy and security of blockchain platforms continues to increase, zero-knowledge proofs are likely to be more widely adopted.Additionally, many Layer 2 protocols on Ethereum are constantly looking for ways to improve scalability and efficiency, and zero-knowledge proofs may help solve these problems.These ongoing efforts will play a key role in protecting user-sensitive information and standardizing blockchain transactions to facilitate blockchain interoperability.