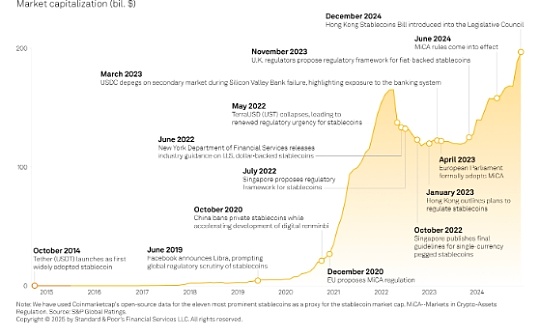
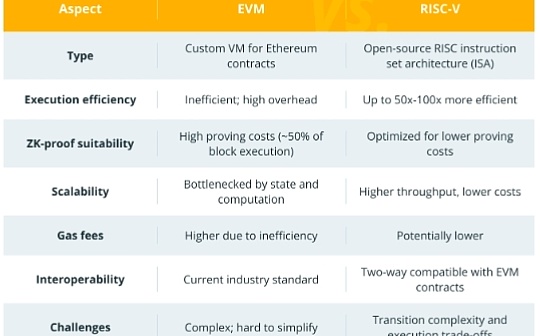
Author: Jagjit Singh, CoinTelegraph; Compiled by: Deng Tong, Bitchain Vision
1. How is Bitcoin priced?
The market power of supply and demand affects the price of Bitcoin.When sellers increase, prices usually drop, and vice versa.
Compared to fiat currencies such as the US dollar, pound, euro and yen, Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency that is not issued by any government or legal authority.To create, store, and transfer BTC, a distributed user network and encryption protocol are required.
Investors conduct business transactions directly, rather than through intermediaries.The peer-to-peer Bitcoin network eliminates trade restrictions and simplifies the business transaction process.Satoshi Nakamoto proposed the world’s first cryptocurrency in 2008 and launched it in January 2009.
The number of businesses that accept Bitcoin helps to improve Bitcoin’s availability and perceived value.However, the price of Bitcoin fluctuates greatly and is subject toThe influence of factors such as media reports, investor sentiment and regulatory news has led to rapid price fluctuations.Even during its most popular period, finding the exact answers to common questions can be challenging, for example, what determines the price of Bitcoin?Who sets the price of Bitcoin?Is Bitcoin intrinsic value?
The supply and demand market dynamics that affect the prices of other goods and services also determine the price of Bitcoin.If there are more buyers than sellers, the price may rise and vice versa.Furthermore, it is worth noting that the price of Bitcoin is not determined by a single entity, nor is it traded at a single location (such as a stock exchange).
Instead, each market or exchange determines its prices based on supply and demand and other factors such as technological advances, security measures and regulatory developments.
2. What factors will affect the price of Bitcoin?
Factors that affect Bitcoin’s price include supply and demand, competition from other cryptocurrencies, news, production costs and regulation.
supply and demand
People with economic backgrounds know the law of supply and demand, that is, supply and demand market forces jointly determine the market price and quantity of a specific commodity.For example, as prices rise and sellers produce more, demand for economic goods falls and vice versa.
The basic economic principles of supply and demand play a crucial role in Bitcoin’s valuation.The supply of Bitcoin has a hard upper limit of 21 million coins, which leads to the scarcity of digital currencies.Once the cap is reached, miners will no longer receive new bitcoins to verify transactions.
Similarly, an event called “Bitcoin Half” cuts the reward for mining new blocks every four years (approximately) and thus reduces the speed at which new Bitcoins enter the market supply.As supply growth slows, if demand remains stable or increases, it could lead to a rise in Bitcoin prices.

Competition and news
Bitcoin competes with numerous cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum (ETH) and Dogecoin (DOGE), each with unique features to attract investors’ interest.In addition, news and media coverage can significantly affect investor sentiment, driving price volatility based on perceptions of Bitcoin’s future prospects.
Production cost
The cost of producing Bitcoin includes not only direct costs such as miners’ infrastructure and electricity, but also indirect costs associated with the complexity of the crypto challenges they must address.These costs help establish a baseline or “break-even” point for miners, affecting the lowest price they think mining bitcoin is economically viable.
In Bitcoin mining, this breakeven point is often referred to as the “base price”, representing the lowest price that can be profitable when mining Bitcoin when considering operating costs.
In addition, the Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of its password puzzles based on overall mining capabilities, thereby affecting the production speed of new Bitcoins.These adjustments may slow down or speed up the creation of Bitcoin, affecting overall supply and, in turn, its market price.
Supervision
Cryptocurrency regulations are constantly changing, with some countries taking a friendly attitude towards cryptocurrencies, such as El Salvador, which made Bitcoin a fiat in 2021, while others have adopted a less friendly attitude towards cryptocurrencies.Regulatory developments could have a significant impact on Bitcoin’s market dynamics, resulting in uncertainty that could affect its price.
When authorities take restrictions, downward pressure on the price of Bitcoin may be put on.Instead, regulatory actions that enhance market access, such as approval of spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in the United States and improving security measures, can promote greater market participation and may lead to higher Bitcoin prices.
3. Why is the price of Bitcoin so fluctuating?
The uncertainty of Bitcoin’s intrinsic value and future price of Bitcoin make it a highly volatile asset.
During the halving period, the number of new bitcoins entering supply steadily decreased every four years, and over time, the inflation rate of assets decreased.According to CompaniesMarketcap , Bitcoin is the tenth largest asset in market capitalization as of this writing, no longer a niche asset, but a significant player in the broader financial sector.In addition, media reports can have a disproportionate impact on asset prices, a phenomenon that is not unique to Bitcoin.
However, driven by digital media and social media platforms, the immediacy and universality of information today means that news (positive or negative) can quickly affect investor sentiment, thus affecting asset prices across the board.This effect is amplified in highly speculative markets, and investor sentiment plays a crucial role, which is often the case with cryptocurrencies.
The approval of the US spot Bitcoin ETF on January 11 had a significant impact on the price of Bitcoin, attracting institutional capital and increasing demand.As of the time of writing, Bitcoin prices have soared 33% since January 11 as traditional financial investors and institutions invest.
Given such high volatility,Can the price of Bitcoin be zeroed?This situation is extremely unlikely, but technically possible under extreme conditions, such as catastrophic technical failures that undermine blockchain security or a complete loss of confidence for all users and investors.However, these situations are extremely unlikely to happen due to the decentralized nature of Bitcoin, the robustness of its widespread adoption and its underlying technology.
Furthermore, a second-tier innovation like Lightning Network is designed to address availability and scalability issues, which can boost Bitcoin’s value proposition.Unlike Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard, which helps create tokens and smart contracts on its network, Bitcoin itself does not support complex smart contracts or token standards by design.
Nevertheless, innovative solutions are under development to expand Bitcoin’s capabilities in the field.For example, development projects such as the RSK (Rootstock) platform are closing this gap by introducing smart contract capabilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Furthermore, the BRC-20 token standard represents an innovative approach to introducing tokenization capabilities directly on the Bitcoin blockchain.As an experimental standard, BRC-20 aims to create, mint and transfer alternative tokens, similar to how the ERC-20 standard operates on Ethereum and other Ethereum virtual machine-compatible networks.
4. How high can Bitcoin actually rise?
The potential future price of Bitcoin is subject to widespread forecasts and speculation, affected by various factors that affect its price trajectory, including determinants such as market adoption, regulatory development, technological advances within the blockchain ecosystem and broader economic conditions..
Market adoption is important becauseThe greater acceptance of Bitcoin by investing and trading can stimulate demand.Governments and financial institutions around the world can help or hinder Bitcoin’s growth through regulatory actions, depending on whether they impose restrictions or provide security and clarity to users.
If technological advances improve Bitcoin’s scalability, security, and use cases, they may have a beneficial impact on the value of Bitcoin.In addition, Bitcoin’s attractiveness as an investment may be affected by macroeconomic variables, including inflation, currency depreciation, and investor sentiment towards traditional and digital assets.
Another aspect to consider is the growing reputation of Bitcoin as “digital gold”, ultimately pushing it to become a store of value and a safe-haven asset.This comparison not only emphasizes Bitcoin’s potential as a hedge against economic volatility, but also illustrates its obvious advantages over traditional investments such as gold due to its digital form and limited supply.
Given these variables, it is challenging to predict the specific value Bitcoin may achieve.Significant fluctuations were observed in historical trends, with corrections mixed during the sharp rise in prices.Using the technology to adopt the S-curve framework, one can predict the future acceptance and growth trajectory of Bitcoin.The model suggests that as Bitcoin develops and overcomes the challenges of initial adoption, it may gain wider acceptance, reflecting the paths taken by other breakthrough technologies.

However, as mentioned above, the theoretical upper limit of Bitcoin price is highly speculative and depends on further progress.Like any investment, potential profits are unguaranteed; therefore, be cautious when speculating on future price fluctuations in Bitcoin.